Middle distance training programs focus on enhancing performance for events like the 800m and 1500m. These structured plans incorporate periodization, progressive overload, and integration of speed and strength to optimize athlete development, ensuring adaptability to individual needs and competitive goals.
Key Components of a Middle Distance Training Program

A middle distance training program focuses on building aerobic endurance, speed, and race-specific strategies. It includes periodization, dividing the season into phases like base building and race preparation. Progressive overload ensures gradual intensity increases to avoid plateaus. Speed and strength training are integrated to enhance economy and endurance. Mental preparation is emphasized to refine race tactics and pacing. Group training fosters competitiveness and accountability, while individualized plans address specific athlete needs. The program balances technical drills, interval workouts, and recovery to optimize performance. Regular feedback and adjustments ensure the program evolves with the athlete’s progress, targeting peak performance during key competitions.

Training Principles for Middle Distance Runners
Consistency, specificity, and recovery are cornerstone principles. Programs balance aerobic development, speed, and strength, ensuring progressive overload to enhance performance while minimizing injury risks and mental fatigue.
Periodization and Progressive Overload in Training
Periodization structures training into phases, each targeting specific goals like building endurance or speed. Progressive overload gradually increases intensity or volume to challenge athletes and avoid plateaus. This approach ensures adaptation, enhancing performance while reducing injury risks. Summer phases focus on base building with higher mileage, transitioning to intensity in fall cross-country seasons. Each cycle incorporates recovery weeks to allow physiological adaptation. Overload is applied through faster repetitions, longer intervals, or increased strength work. Proper periodization balances stress and recovery, ensuring peak performance during key competitions. This systematic approach is essential for middle distance athletes to achieve long-term success and sustainability in their training.

Integrating Speed and Strength Training into the Program
Speed and strength training are crucial for middle distance runners to enhance power and efficiency. Sprinting sessions improve leg speed and economy, while strength exercises like cleans and plyometrics build explosive power. These workouts prevent injuries and boost race performance. Strength training is typically done 2-3 times weekly, focusing on lower-body exercises and core stability. Speed work includes short, fast repetitions with recovery periods. This dual approach ensures athletes can maintain speed during races and handle training demands. Combining these elements creates a balanced program that addresses both endurance and speed needs, ultimately improving overall competitiveness.
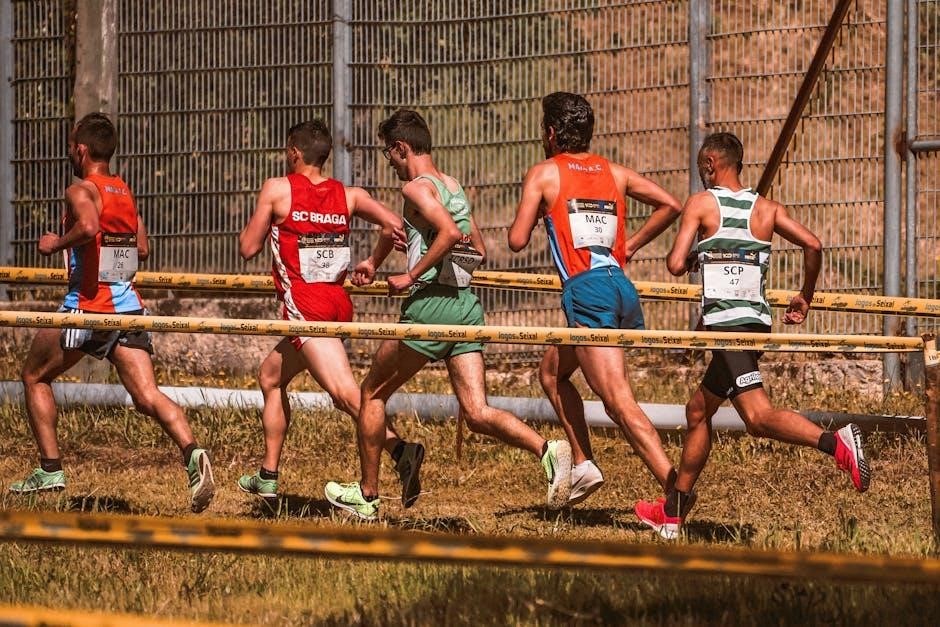

Workouts and Exercises for Middle Distance Athletes
Workouts include interval training, tempo runs, and hill repeats to build endurance and speed. Long runs enhance stamina, while strides improve running efficiency and form.
Specific Pace Workout Examples for 800m and 1500m Events
For 800m and 1500m events, specific pace workouts are designed to enhance race-specific fitness. Examples include 3-5 sets of 400m at mile effort with 1-minute recovery and 200m at 800m effort with 4-5 minutes between sets. These workouts aim to build lactate threshold and speed endurance, simulating race conditions. Additionally, tempo runs at goal pace and interval training with varying distances and intensities are used to improve running efficiency and mental toughness. Strength training, such as cleans and box jumps, is also incorporated to enhance power and endurance. These workouts are periodized to ensure progressive overload, preventing overtraining and maximizing performance. By focusing on race-specific paces and recovery, athletes develop the ability to maintain form and composure during critical race moments.

Role of Interval Training in Building Endurance and Speed
Interval training is a cornerstone of middle distance programs, designed to enhance both endurance and speed. It involves repeating short to medium distances at race pace or faster, with structured recovery periods. For example, 300m, 200m, or 100m repeats are common, with 1-2 minutes of rest between efforts. These workouts target lactate threshold improvement, allowing athletes to sustain faster paces longer. Interval sessions also build mental resilience and race-specific stamina. By progressively increasing intensity and reducing recovery time, runners adapt to the demands of racing. This method ensures a balance between aerobic and anaerobic development, making it essential for achieving peak performance in the 800m and 1500m events. Consistency in interval training is key to unlocking endurance and speed gains.

Mental and Tactical Aspects of Middle Distance Training
Mental preparation and tactical strategies are vital for middle distance success. Training each race phase enhances focus and execution, while group training fosters competitiveness and resilience.
Training Each Phase of the Race for Optimal Performance

Breaking the race into distinct phases—start, middle, and finish—is crucial for middle distance runners. The start focuses on positioning and explosive speed, while the middle emphasizes maintaining pace and mental resilience. The finish requires strategic pacing and a strong sprint. Workouts like interval training and tempo runs simulate race conditions, helping athletes master each phase. Mental strategies, such as visualization and positive self-talk, enhance focus during intense moments. Group training also plays a role, fostering competitiveness and adaptability. By periodizing training to address each phase, runners build confidence and tactical awareness, ensuring peak performance on race day. This structured approach ensures athletes are prepared for every segment of the race, from the initial burst to the final sprint.

Group Training Strategies to Enhance Competitiveness
Group training is a powerful tool for fostering competitiveness among middle distance runners. Training with teammates encourages accountability, motivation, and camaraderie, pushing athletes to perform at their best. Workouts like interval training, tempo runs, and relays simulate race conditions, allowing runners to practice pacing and strategy together. Group sessions also provide opportunities to learn from others, adopt new techniques, and build mental toughness. Coaches can design workouts that cater to different fitness levels while promoting healthy competition. Periodization ensures that group training progresses gradually, avoiding burnout and keeping athletes engaged. By training collectively, runners develop the resilience and tactical awareness needed to excel in competitive races, making group sessions an essential component of a successful middle distance program.
A well-structured middle distance training program enhances performance and competitiveness. Regular evaluation ensures effectiveness, with adjustments made based on athlete feedback and progress to optimize results.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Training Program
Evaluating a middle distance training program involves assessing race performance, physiological adaptations, and athlete feedback. Key metrics include improvements in race times, endurance, and speed. Coaches should monitor progress through periodic tests, such as time trials or interval assessments. Feedback from athletes provides insights into program satisfaction and areas for refinement. Physiological measures, like heart rate and lactate thresholds, can indicate aerobic and anaerobic improvements. Additionally, injury rates and consistency in training are crucial indicators of program effectiveness. By combining these elements, coaches can determine if the program successfully enhances performance and achieves competitive goals. Adjustments are then made to optimize future training cycles and ensure continued progress for athletes.
Adapting the Program Based on Athlete Feedback and Progress
Adapting a training program based on athlete feedback and progress ensures personalized development and maximizes performance gains. Regular communication with athletes helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and training preferences. Coaches can adjust workout intensity, volume, or recovery periods to address individual needs. Progress monitoring, such as race results and physiological tests, guides modifications to training cycles. If an athlete excels in speed work, more specialized sessions can be added, while others may benefit from increased endurance focus. Flexibility in the program fosters engagement and reduces injury risks. Continuous adjustments ensure the training remains challenging yet achievable, keeping athletes motivated and aligned with their competitive goals throughout the season. This dynamic approach is essential for long-term success in middle distance events.